Redux 使用及原理
简单简述Redux使用以及原理
为何需要使用 redux
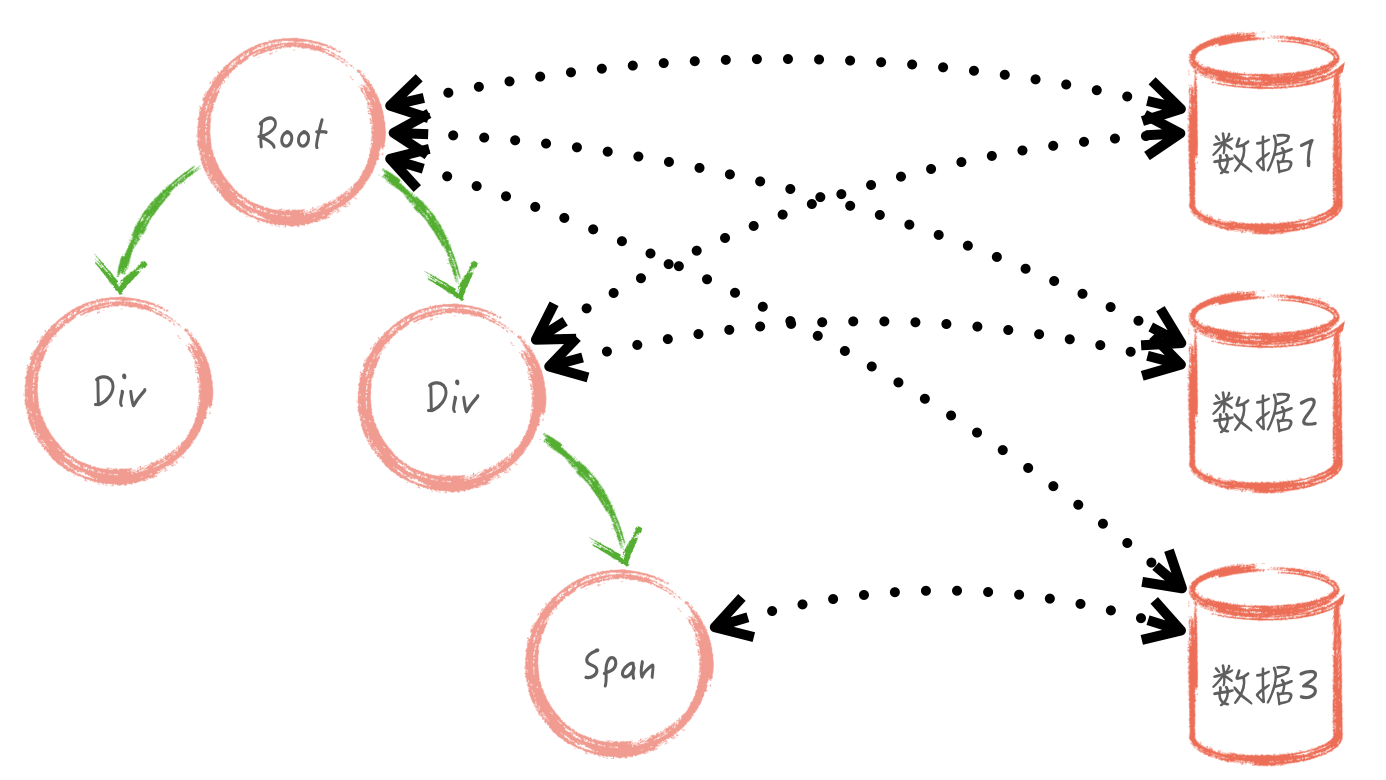
当下的 Web 应用越来越复杂,数据状态也愈来愈多。常如下图所示,无法知晓是哪里修改了数据,一个视图使用了多个地方的数据,无法统一进行控制。
加入 redux 后,思路将变的清晰明了,数据源只有一个,数据只能通过 dispatch 使用特定的 action 进行修改。这样的数据是单向的,有利于统一控制与调试。
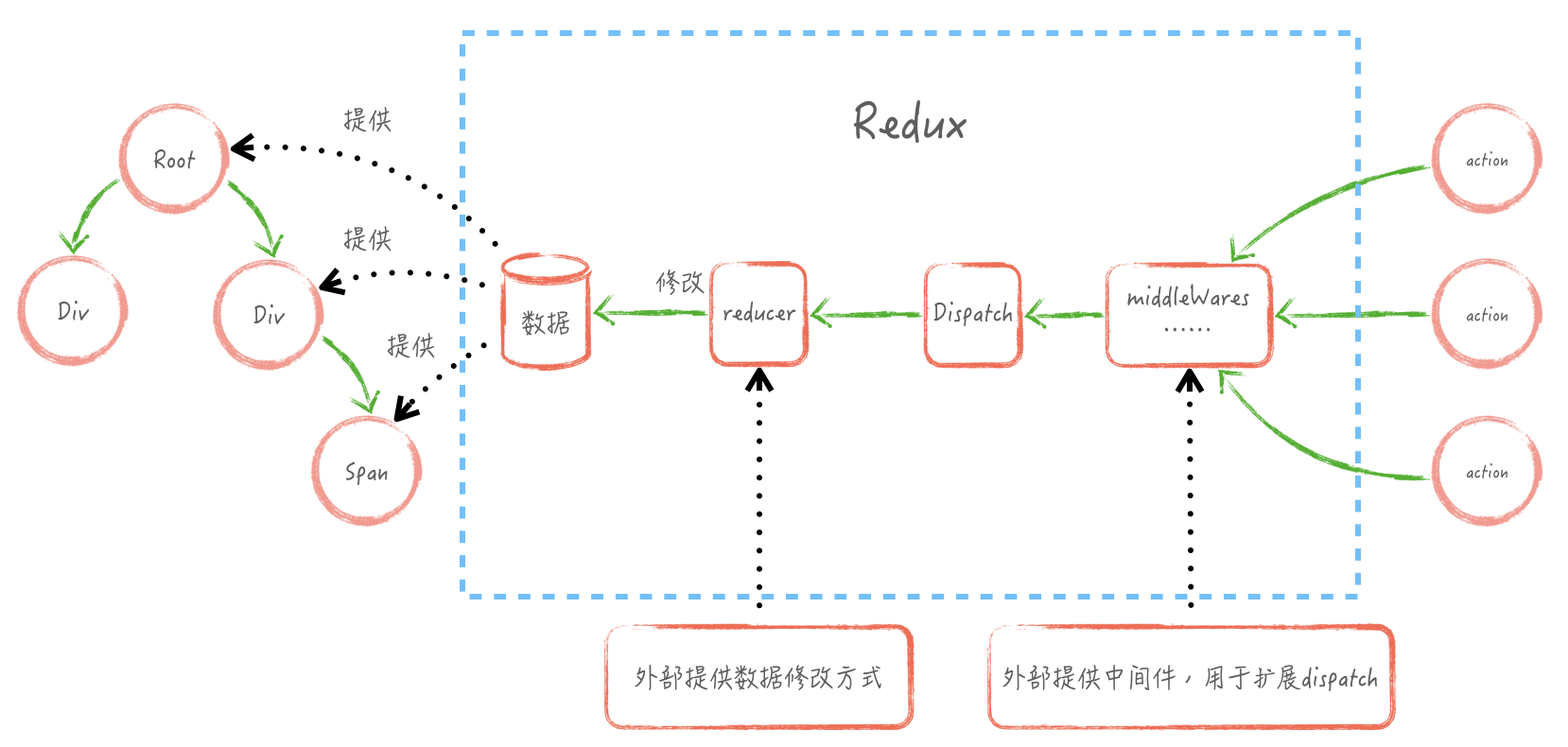
Redux 使用
在 UI 视图中使用一个数据,需要的基本能力有读取数据、修改数据、监听数据的能力,redux 也不例外。redux 把这几种能力封装至 Store 中,对应上图的数据部分。
redux 对应上述的几种能力对应的 API 如下:
- 读取数据:getState()
- 修改数据:dispatch(action)
- 监听数据:subscribe(listener)
其中修改数据在每个应用中的规则都是不同的,因此需要开放一个接口给每个应用设置不同的修改规则。对应上图中的‘reducer’部分;
下面使用计数器例子演示如何使用 redux。
import React from 'react';
import { AnyAction, createStore } from 'redux';
// 数据的修改规则
function reducer(state: any = { count: 1 }, action: AnyAction) {
switch (action.type) {
case '@count/add':
return { ...state, count: (state.count += 1) };
case '@count/reset':
return { ...state, count: 0 };
default:
return state;
}
}
// 创建数据源
const Store = createStore(reducer);
export default class extends React.Component {
public componentDidMount() {
// 数据源变化,更新视图
Store.subscribe(() => this.forceUpdate());
}
public render(): React.ReactNode {
// 读取数据
const { count } = Store.getState();
return (
<div>
<p>{count}</p>
<button onClick={() => Store.dispatch({ type: '@count/add' })}>加一</button>
<button onClick={() => Store.dispatch({ type: '@count/reset' })}>重置</button>
</div>
);
}
}
实现 DRedux
要实现 redux 最重要的就是实现 Store 上的三个方法
export function createStore<S, P>(reducer: Reducer<S, P>) {
function getState() {}
function dispatch(action: Action<P>) {}
function subscribe(listener: () => void) {}
return {
// 获取store中的状态
getState,
// 更新store的状态,并派发更新事件
dispatch,
// 监听store的状态变化
subscribe,
};
}
getState 是读取当前状态的,可以如下实现:
export function createStore<S, P>(reducer: Reducer<S, P>) {
let state: S;
function getState() {
return state;
}
function dispatch(action: Action<P>) {}
function subscribe(listener: () => void) {}
return { getState, dispatch, subscribe };
}
subscribe 是用于注册状态变更后触发的事件,可以如下实现:
export function createStore<S, P>(reducer: Reducer<S, P>) {
let state: S;
let listeners: (() => void)[] = [];
function getState() {...}
function dispatch(action: Action<P>) {...}
function subscribe(listener: () => void) {
listeners.push(listener);
}
return { getState, dispatch, subscribe };
}
dispatch 作用是当前状态按照 reducer 规则计算出新的状态并修改当前状态,接着触发注册的监听事件,可以如下实现:
export function createStore<S, P>(reducer: Reducer<S, P>) {
let state: S;
let listeners: (() => void)[] = [];
function getState() {...}
function dispatch(action: Action<P>) {
// 计算并修改当前状态
state = reducer(state, action);
// 触发监听事件
listeners.forEach((listner) => listner());
}
function subscribe(listener: () => void) {...}
return { getState, dispatch, subscribe };
}
reducer 中的第一个参数有初始化值,所以需要默认调用一次 dispatch 来获取 reducer 中的初始化值,如下代码所示。
export function createStore<S, P>(reducer: Reducer<S, P>) {
let state: S;
let listeners: (() => void)[] = [];
function getState() {...}
function dispatch(action: Action<P>) {...}
function subscribe(listener: () => void) {...}
dispatch({ type: Symbol('@dredux/init') }); // 使用Symbol避免与 reducer 中的type重复
return { getState, dispatch, subscribe };
}
接下使用自己实现的 DRedux 替换计数器中的 Redux
import React from 'react';
import { AnyAction, createStore } from './dredux';
// 数据的修改规则
function reducer(state: any = { count: 1 }, action: AnyAction) {
switch (action.type) {
case '@count/add':
return { ...state, count: (state.count += 1) };
case '@count/reset':
return { ...state, count: 0 };
default:
return state;
}
}
// 创建数据源
const Store = createStore(reducer);
export default class extends React.Component {
public componentDidMount() {
// 数据源变化,更新视图
Store.subscribe(() => this.forceUpdate());
}
public render(): React.ReactNode {
// 读取数据
const { count } = Store.getState();
return (
<div>
<p>{count}</p>
<button onClick={() => Store.dispatch({ type: '@count/add' })}>加一</button>
<button onClick={() => Store.dispatch({ type: '@count/reset' })}>重置</button>
</div>
);
}
}
- 为何需要使用 redux
- Redux 使用
- 实现 DRedux